Relational databases are treasure troves of information, but extracting meaningful insights often requires deep technical expertise in statistics and database languages. Manual analysis or configuring purpose-built models can be complex, inflexible, and time-consuming. What if we could simply ask questions in natural language and get back insightful analysis and visualizations?
This granted patent (US 12,254,015 B1) introduces a system designed to do just that, leveraging the power of Generative Artificial Intelligence (AI) language models.
Key Takeaways
- Uses Generative AI to understand natural language queries about relational databases.
- Intelligently selects relevant data subsets, overcoming AI token limits.
- Employs techniques like denormalization, correlation analysis, and data aggregation.
- Generates both textual insights and data visualizations automatically.
- Makes complex data analysis accessible to non-technical users.
The Challenge: Bridging Databases and AI
While Generative AI excels at understanding language and generating text, applying it directly to large relational databases presents hurdles. A major challenge is the prompt token limit inherent in many AI models -- the sheer volume of raw database data often exceeds what the AI can process at once.
Furthermore, users might not know the exact terms or correlations needed to formulate the most effective query. Traditional methods often provide narrow answers, lacking a holistic view.
The Patented Solution: A Multi-Step AI Approach
The core idea is a system that intelligently uses a Generative AI model in multiple stages, combined with smart data processing techniques. The diagram below gives a visual overview of the workflow:
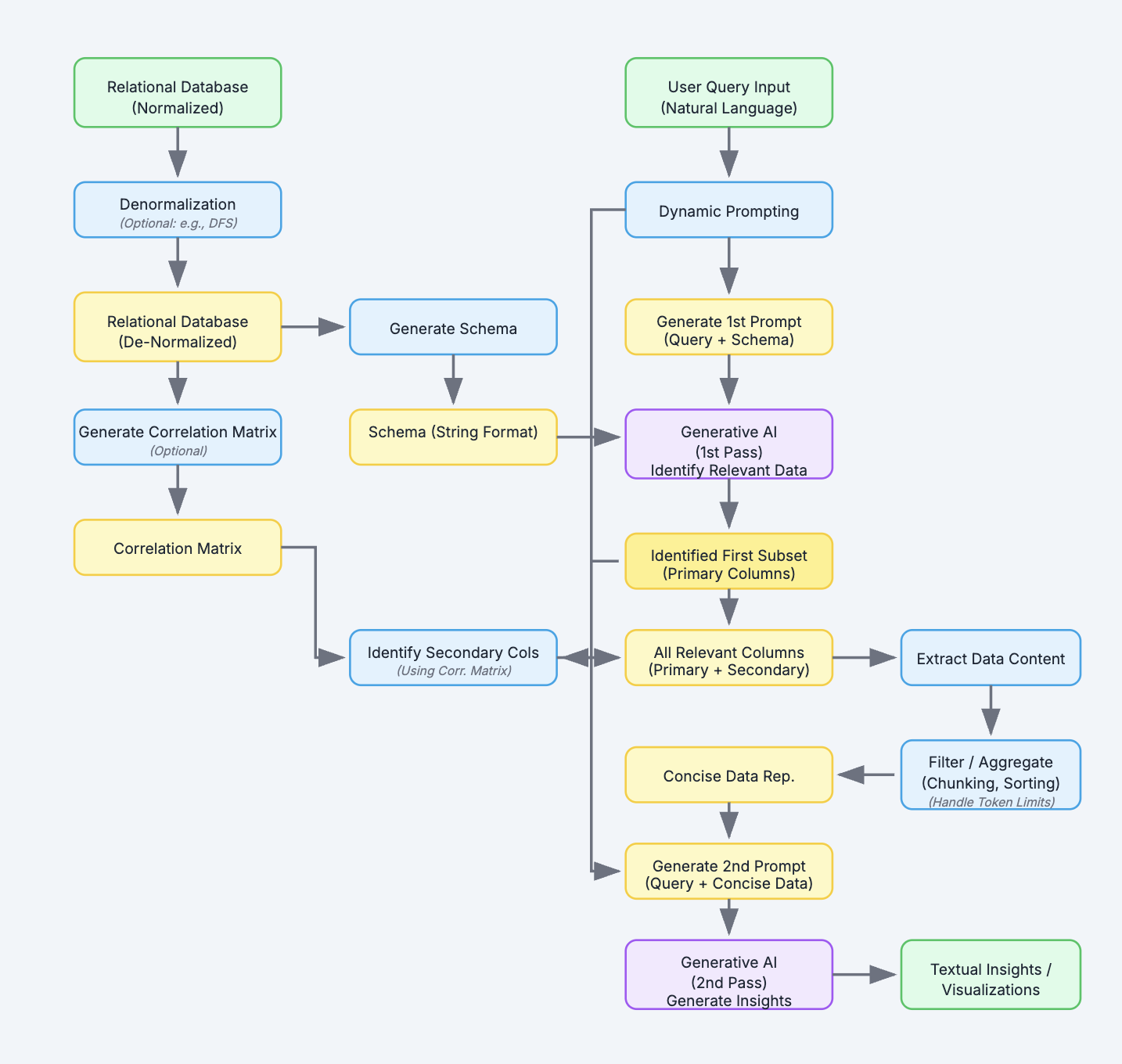
Here is how the workflow operates:
Step 1: Receive Data and Generate Schema
The system ingests relational database data. It then analyzes the structure (tables, columns, types) and creates a simplified text description (schema) for the AI.
- Input: Raw Database Data
- Output: Schema in Text Format
Step 2: Understand the User Query
A user asks a question in plain English (e.g., "Show sales trends by region"). The system might use Dynamic Prompting to refine this query, adding context or keywords like revenue or visualize before sending it to the AI.
- Input: Natural Language Query
- Output: Enhanced Query for AI
Step 3: First AI Pass -- Identify Relevant Data
The enhanced query and the text schema are sent to a Generative AI. The AI identifies the most relevant tables and columns (the first subset or primary columns) needed to answer the query.
- Input: Enhanced Query, Text Schema
- Output: List of Primary Columns
Step 4: Data Processing and Reduction
This stage prepares the data for the AI and manages size constraints.
-
(Optional) Denormalization: Combines related tables for easier analysis.
-
(Optional) Correlation Analysis: Finds secondary columns strongly related to the primary ones, adding potentially relevant context.
-
Content Extraction: Retrieves the actual data values for all identified relevant columns.
-
Compression: Filters out less useful data (e.g., high-cardinality text) and aggregates numerical data (e.g., using averages within sorted "chunks") to create a concise representation that fits within AI token limits while preserving key trends.
-
Input: Primary Columns, (Optional) Correlation Matrix, Database Content
-
Output: Concise Data Representation
Step 5: Second AI Pass -- Generate Insights
The user's query and the compact, concise data representation are sent to the Generative AI again.
- Input: Enhanced Query, Concise Data
- Output: Insight Data (Text/Visual Specs)
Step 6: Receive Output
The AI returns the generated insights, which can be text summaries, explanations of patterns, or specifications for creating visualizations (like charts and graphs), potentially generated by the AI itself or a separate visualization tool.
- Input: Insight Data from AI
- Output: User-facing Text and Visualizations
Why This Matters
This patented approach offers several advantages:
- Accessibility: Lowers the technical barrier, allowing users without database language expertise to derive insights.
- Comprehensive Analysis: Goes beyond the user's explicit query by incorporating correlated data, providing a broader understanding.
- Scalability: Addresses AI token limitations through intelligent data reduction, enabling analysis of large datasets.
- Rich Output: Delivers insights in both textual and easy-to-understand visual formats.
Conclusion
By cleverly combining data preprocessing, correlation analysis, data reduction, and multiple passes through a Generative AI model, this system offers a powerful new way to interact with and understand relational database data. It democratizes data analysis, making sophisticated insights accessible through simple natural language questions.
Patent: US 12,254,015 B1
